B Sc III Sex Determination Concept
I. The Chromosome Theory of Inheritance and Sex Linkage
A. Sutton and Boveri’s chromosome theory of inheritance proposed in 1902—Genes are located on chromosomes
B. Just previous to this (end of 19th century) biologists had discovered that half of all sperm cells carry a structure called an X body.
C. In 1905 the X bodies were determined to be chromosomes—X chromosomes.
D. Then the Y chromosome was also discovered in 1905.
E. Together the X and Y chromosomes are known as the sex chromosomes.
F. All other chromosomes are called autosomes.
G. Systems of sex chromosomes
2) XX-XY System (S H 5)
(a) Female—XX (homogametic sex)
(b) Male XY (heterogametic sex)
(c) Occurs in Drosophila, mammals and some plants
3) ZZ-ZW System(S H 5)
(a) Female—XY (heterogametic sex)
(b) Male—XX (homogametic sex)
(c) Occurs in birds, butterflies and some fishes
4) X-Y-XY System(S H 5)
(a) Occurs in organisms with alteration of generations (e.g., liverworts and vascular plants)
(b) Male gametophytes—Y
(c) Female gametophytes—X
(d) Sporophytes—XY
(b) Differential region
(i) Differential regions do not pair during synapsis
(ii) Differential region genes are either
1. X-linked
2. Y-linked
(iii) Any gene X or Y chromosome is said to be sex linked.
1) Sex is determined by the ratio of the number of X chromosomes to number of autosomal sets
2) Scheme
(a) X/A = 1.0—female
(b) X/A = 0.5—male
(c) X/A > 1.0—metafemale
(d) X/A < 0.5—metamale
• The presence or absence of the Y chromosome determines sex
• XX determines the female and XY determines the male.
Source: http://english.eagetutor.com/home/sex-determination-system-sp-193278729
Development of sexual characteristics


A sex-determination system is a biological system that determines the development of sexual characteristics in an organism. Two sexes are present in most sexual organisms. Because of the sexual chromosome differences the sex determination.
SEX DETERMINATION AND SEX CHROMOSOMES
I. The Chromosome Theory of Inheritance and Sex Linkage
A. Sutton and Boveri’s chromosome theory of inheritance proposed in 1902—Genes are located on chromosomes
B. Just previous to this (end of 19th century) biologists had discovered that half of all sperm cells carry a structure called an X body.
C. In 1905 the X bodies were determined to be chromosomes—X chromosomes.
D. Then the Y chromosome was also discovered in 1905.
E. Together the X and Y chromosomes are known as the sex chromosomes.
F. All other chromosomes are called autosomes.
G. Systems of sex chromosomes
1) XX-XO system (S H 5)
(a) Female—XX
(b) Male—X
(c) Occurs in some insects like grasshoppers
(a) Female—XX
(b) Male—X
(c) Occurs in some insects like grasshoppers
2) XX-XY System (S H 5)
(a) Female—XX (homogametic sex)
(b) Male XY (heterogametic sex)
(c) Occurs in Drosophila, mammals and some plants
3) ZZ-ZW System(S H 5)
(a) Female—XY (heterogametic sex)
(b) Male—XX (homogametic sex)
(c) Occurs in birds, butterflies and some fishes
4) X-Y-XY System(S H 5)
(a) Occurs in organisms with alteration of generations (e.g., liverworts and vascular plants)
(b) Male gametophytes—Y
(c) Female gametophytes—X
(d) Sporophytes—XY
H. Morphology and pairing of X and Y
1) Each type of sex chromosome has two regions
(a) Pairing region
(i) During synapsis of meiotic prophase I, the pairing regions combine
(ii) Some genes occur in these pairing regions
(iii) These genes exhibit X-and-Y linkage

1) Each type of sex chromosome has two regions
(a) Pairing region
(i) During synapsis of meiotic prophase I, the pairing regions combine
(ii) Some genes occur in these pairing regions
(iii) These genes exhibit X-and-Y linkage
(b) Differential region
(i) Differential regions do not pair during synapsis
(ii) Differential region genes are either
1. X-linked
2. Y-linked
(iii) Any gene X or Y chromosome is said to be sex linked.
I. Sex determination in Drosophila
1) Sex is determined by the ratio of the number of X chromosomes to number of autosomal sets
2) Scheme
(a) X/A = 1.0—female
(b) X/A = 0.5—male
(c) X/A > 1.0—metafemale
(d) X/A < 0.5—metamale
J. Sex determination in humans

• The presence or absence of the Y chromosome determines sex
• XX determines the female and XY determines the male.
Source: http://english.eagetutor.com/home/sex-determination-system-sp-193278729
Sex determination in humans:
In human beings, sex is determined by genetic inheritance. Genes inherited from the parents determine whether an offspring will be a boy or a girl.
Genes for all the characters are linearly arranged on chromosomes. These include the genes for sexual characters.
Generally, characters related to the reproductive system are called sexual characters and those that are not are called vegetative characters. The chromosomes that carry genes for sexual characters are called sex chromosomes, while those that carry genes for the vegetative characters are called autonomies.
A sex chromosome that carries the genes for male characters is called Y chromosome and one which carries the genes for female characters is called X Chromosome.
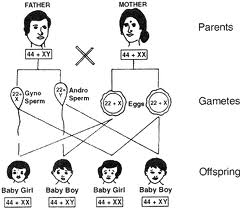
We have a total of 46 chromosomes. Half of them come from the mother and the rest, from the father. Out of these 46 chromosomes, 44 are autonomies and 2 are sex chromosomes. The sex chromosomes are not always a perfect pair.
In females there are 44 autonomies and two X chromosomes, in males there are 44 autonomies, one X chromosome and one Y chromosome. So the chromosomes
In woman are 44 + XX, while the chromosomes in man are 44 + XY. Let us see the inheritance pattern of X and Y chromosomes.
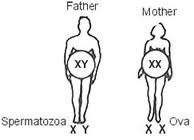
During gamete formation, the normal diploid chromosome number is halved. This is called the haploid condition. All the eggs of a female have 22 + X chromosomes. A male produces two types of sperms—one type bears the 22 + X composition and the other, 22 + Y. Therefore, in every 100 sperms, 50 have Y chromosomes and 50 have X chromosomes.
Any one of the two types of sperms can fertilize the egg. If a Y-bearing sperm fertilizes the egg, the zygote has the 44 + XY composition, and the resulting embryo grows to be a boy. When an X-bearing sperm fertilizes the egg, the resulting zygote has the 44 + XX composition. This embryo develops into a girl. All the children inherit one X chromosome from the mother.
Therefore, sex is always determined by the other sex chromosome that they inherit from the father. One who inherits the X chromosome of the father is a girl, while one who inherits the Y chromosome of the father is a boy.
Role of environment in sex determination:
Environmental conditions such as temperature around the developing embryo may determine sex in some animals. Such conditions may override the genetic basis. Some animals such as snails can even change their sex, showing that their sex is not genetically determined.
Incubation of the eggs of the turtle Chrysema picta at a high temperature produces females. But the incubation of the eggs of the lizard Agama at a high temperature produces males.
http://www.biologydiscussion.com/essay/determination-of-sex-in-human-beings/1643
No comments:
Post a Comment