B Sc II
Development of Male gametophyte (Before pollination):
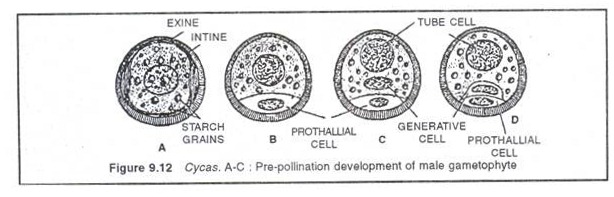
Microspore or pollen grain is the first cell of the gametophyte. The microspore germinates in situ i.e. while within the microsporangium. Each microspore divides asymmetrically into a 2-cells: a smaller prothallial cell and a larger antheridialcell. The prothallial cell does not divide further while the antheridial cell divides into a smaller generative cell near the prothallial cell and a larger tube cell. Finally pollination takes place at 3-celled stage (a prothallial cell, a generative cell and a tube nucleus) (Fig. 9.12).
Pollination:
In Cycas pollination is anemophilous (by wind). The 3-celled microspores liberate from mega-sporangia are blown away by wind. Finally microspores reach on ovules and get enlarged in the pollination drop (ooze) of micropyle. As the ooze dries up, the microspores are drawn into the pollen chamber.
(d) Development male Gametophyte (After pollination):
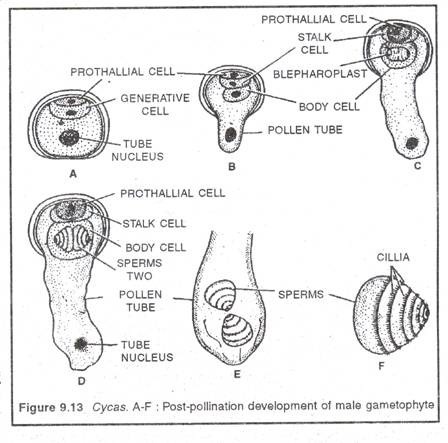
After a gap of about 4 months, post-pollination development of male gametophyte occurs. The exine ruptures and the intine grows out in form of apollen tube. The pollen tube acts as a haustorium, i.e. absorb food while penetrating through the nucellus and hang in the archegonial chamber. In the pollen tube, generative cell divides into a stalk cell and a body cell. Finally, the body cell divides into two male gametes or antherozoids. Thus, a fully developed male- gametophyte consists of a disorganized prothallial cell, stalk cell, tube nucleus and 2 male gametes (Fig 9.13 )
Each male gamete appears top-shaped with 5-6 spiral bands of cilia. The size of male gamete in Cycas varies from 180-210µm (largest, 400«m reported from Chigua, a cycad).
Source : http://www.biologydiscussion.com/life-cycle/life-cycle-of-cycas-vegetative-and-sexual-life-cycle/5766
Development of female gametophyte (Endosperm):
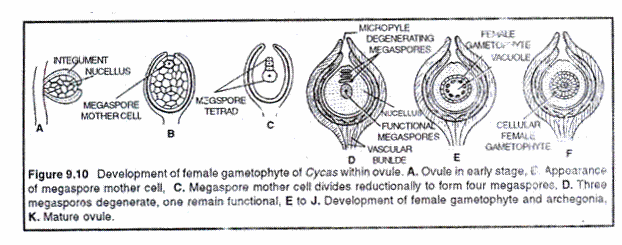
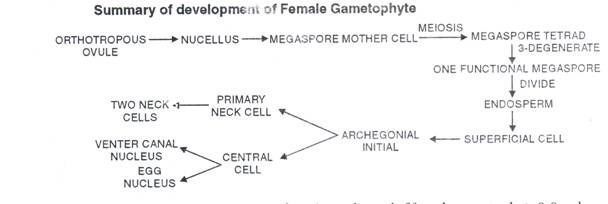
Inside the nucellus, one cell differentiated into megaspore mother cell. It undergoes reduction division (meiosis) to form a linear tetrad of four haploid megaspores. Usually, the upper 3 megaspores towards micropyle degenerate while the lower most functional megaspore (embryo sac cell) undergoes free nuclear division followed by wall formation to form a cellular female gametophyte or endosperm.
Hence, the formation of female gametophyte is monosporic, i.e develops from a single megaspore. During formation of endosperm nucellus is utilized. It should be noted that in gymnosperms the endosperm develop before fertilization and is haploid (n) while in angiosperms it is triploid (3n) and formed after fertilization (Fig. 9.10).
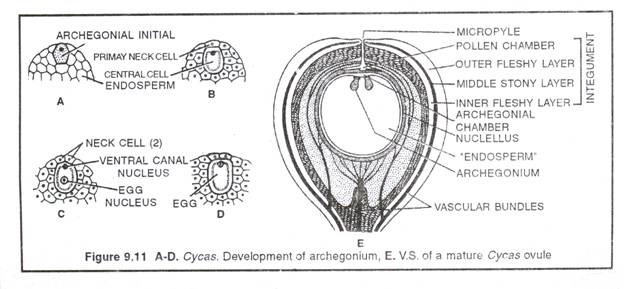
At the micropylar end of female gametophyte 2-8 archegonia develop. All the necks of archegonia open into an archegonial chamber formed by a depression in female gametophyte (Fig. 9.11). Each archegonium develops from single superficial cell called archegonial initial.
It gets enlarged and divides transversally into outer primary neck cell and inner central cell. The primary neck cell divides anticlinally to form two neck cells. The inner central cell enlarges and its nucleus divides into venter canal nucleus and egg nucleus. Soon the venter canal nucleus disorganizes. Thus, a mature archegonium has two neck cells and an egg. Neck canal cells are not formed. The egg cell in Cycas is largest in the plant kingdom (Fig. 9.11).
Source : http://www.biologydiscussion.com/life-cycle/life-cycle-of-cycas-vegetative-and-sexual-life-cycle/5766
No comments:
Post a Comment